1. INTRODUCTION
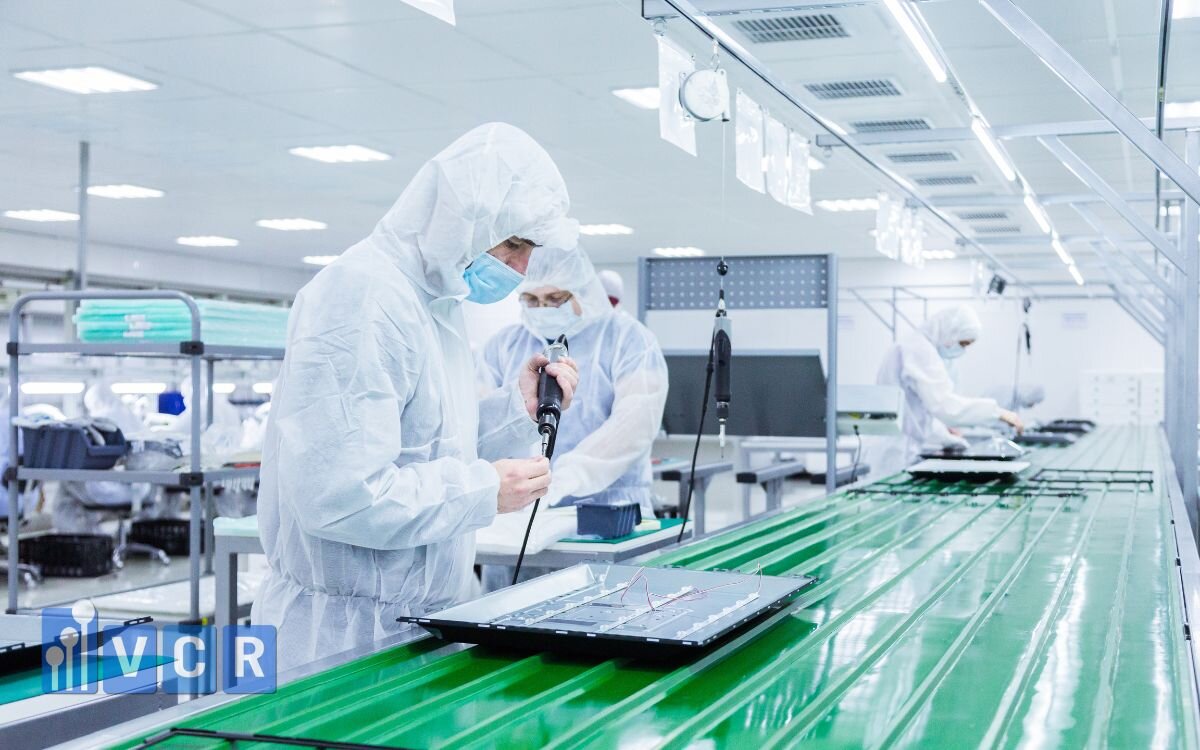
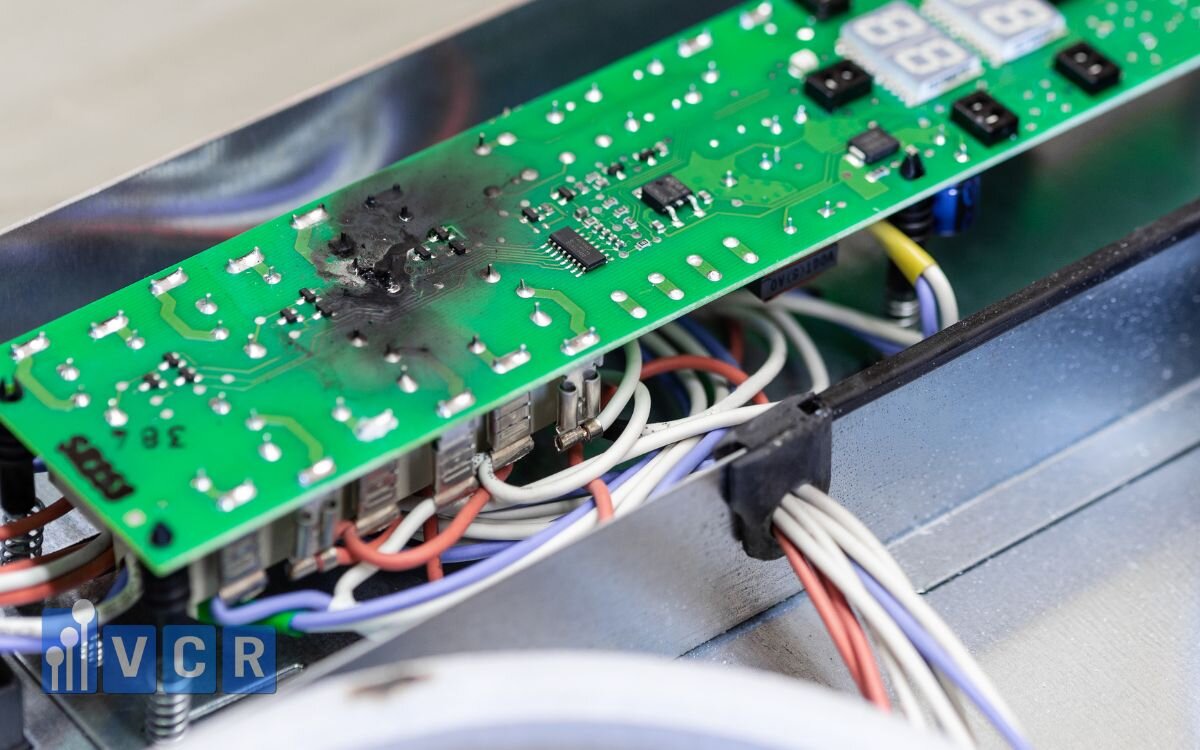
In the electronics cleanroom environment—where microchips, PCBs, ICs, and semiconductor devices are manufactured and assembled—electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a constant hidden threat. A tiny, invisible electrostatic spark can damage sensitive circuits, cause product malfunctions, and lead to significant losses for manufacturers. Thus, controlling and dissipating static electricity from surfaces like equipment, workbenches, floors, racks, and carts is mandatory, as required by international standards like IEC 61340 and ANSI/ESD S20.20.
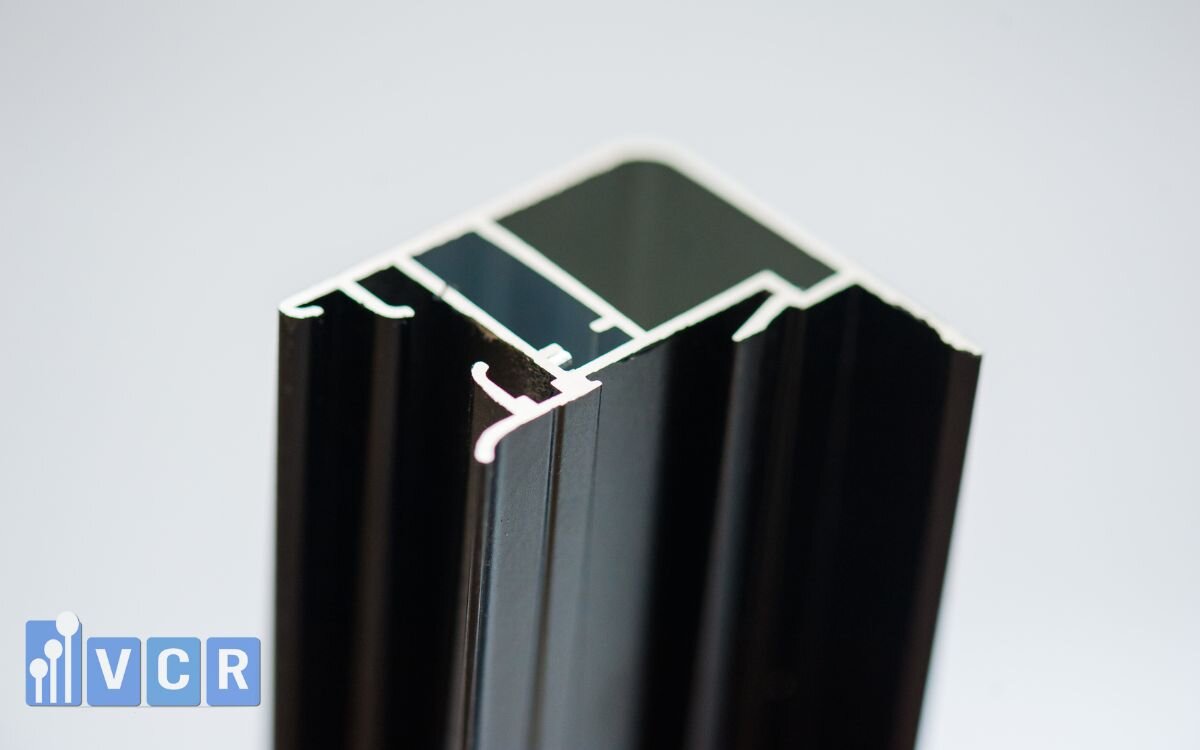
Among the available ESD coating solutions, two technologies are most widely discussed: ESD powder coating and conductive anodizing. These methods have different approaches: one involves applying a conductive coating, while the other transforms the aluminum surface into a special conductive oxide layer.
So, which is the optimal choice for electronics cleanrooms? ESD powder coating offers easier application and reasonable cost, while conductive anodizing provides high-end aesthetics and durability but comes at a higher price. This article will provide a detailed analysis—from process, technical specifications, and applications to cost—helping you determine the most effective ESD control solution for your electronics facility.
2. ESD ISSUES IN ELECTRONICS CLEANROOMS
In electronics factories, ESD is the “invisible enemy” of components. When an operator, tool, or surface becomes charged and releases even a small discharge, it can:
-
Instantly destroy sensitive components (ICs, transistors, diodes).
-
Degrade component reliability, causing failures after a period of use.
-
Increase defect rates, resulting in financial loss and damaged brand reputation.
In reality, a discharge of just a few hundred volts (undetectable to humans) is enough to damage a semiconductor chip. When you touch a doorknob and feel a “shock,” that’s already around 2,000-3,000 volts—highlighting how dangerous ESD can be in production environments.
International standards such as IEC 61340 (Electrostatics) and ANSI/ESD S20.20 (ESD Control Program) clearly state that in electronics cleanrooms, surface resistivity of equipment, floors, workbenches, and storage must fall within a safe range (10⁵ to 10⁹ Ω) to ensure effective static discharge.
Thus, applying ESD coatings to surfaces—including benches, racks, carts, and aluminum module casings—has become mandatory. Among current solutions, ESD powder coating and conductive anodizing are the most prominent, each offering unique advantages in performance, cost, and application.
3. ESD POWDER COATING
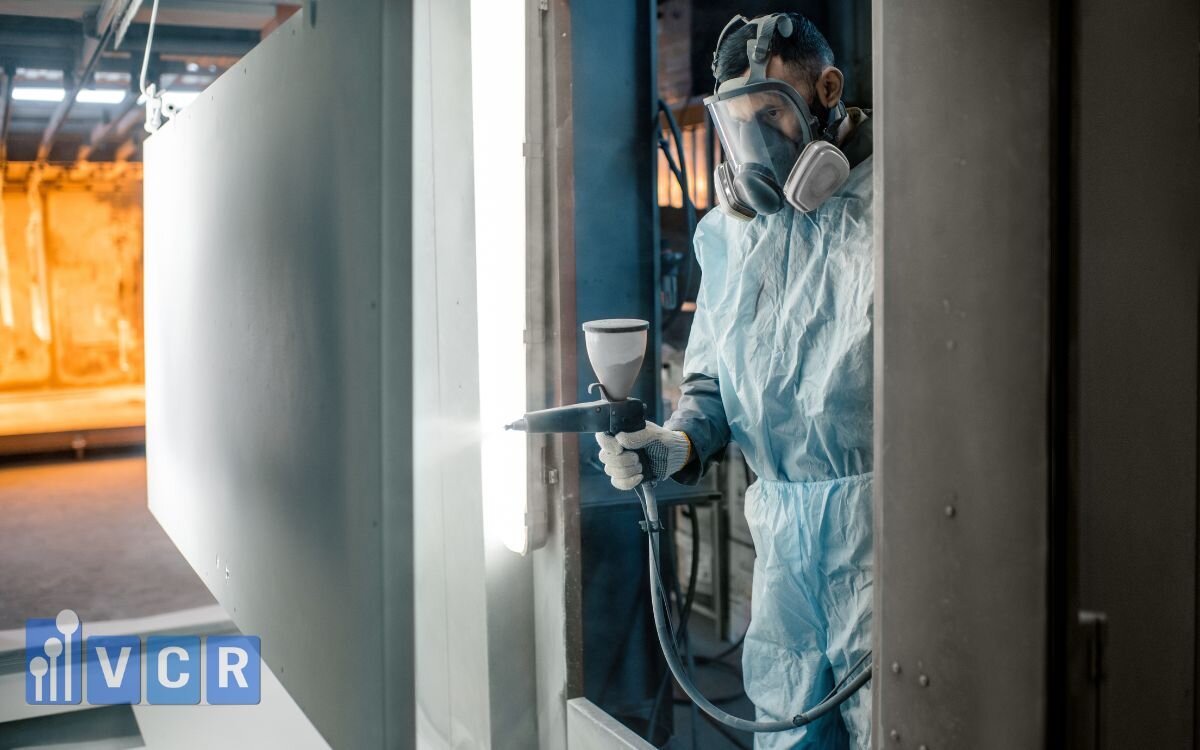
3.1 What is ESD powder coating?
ESD powder coating (Electrostatic Discharge Powder Coating) is a specialized type of powder coating designed to dissipate static charges instead of insulating them. While traditional powder coatings are highly resistive (non-conductive), ESD powder coatings include conductive additives such as carbon black, carbon fibers, or dedicated ESD agents. This enables the coated surface to maintain a surface resistivity between 10⁵ and 10⁹ Ω, compliant with IEC 61340 and ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards.
3.2 Production process & surface resistivity
The ESD powder coating process is similar to that of conventional powder coating:
-
Surface pre-treatment: Cleaning of oils, dust, and rust using chemicals and DI water.
-
ESD powder application: Electrostatic spray guns apply the charged powder onto metal surfaces.
-
Curing: The powder is melted and cured at 180-200°C, forming a seamless coating.
The key difference lies in the powder itself: unlike pure polyester or epoxy, ESD powder includes conductive additives to allow controlled dissipation of electrical charges.
3.3 Applications in electronics cleanrooms
ESD powder coating is widely used on surfaces of cleanroom equipment and tools, such as:
-
ESD workbenches: Dissipate charges from operators assembling components.
-
ESD carts & racks: Safely transport sensitive components without generating static.
-
PCB cabinets, board racks: Protect circuit boards from ESD damage.
-
ESD flooring: Used with anti-static floor coatings or ESD vinyl tiles to control surface voltage.
3.4 Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
-
Easy to apply on various metals (steel, aluminum).
-
Cost-effective, suitable for mass production.
-
Greater color variety compared to conductive anodizing.
-
Meets ESD requirements in diverse electronics environments.
Disadvantages:
-
Thick coating layer, susceptible to chipping under impact.
-
Shorter lifespan than anodizing (typically needs recoating after 5-10 years).
-
Requires regular resistivity testing, as ESD properties may degrade over time or in humid conditions.
Summary:
ESD powder coating is the most common anti-static solution for benches, racks, carts, and floors in electronics cleanrooms due to its cost-effectiveness and reliable surface resistivity control. However, for premium, long-lasting finishes, conductive anodizing remains a high-end alternative.
4. CONDUCTIVE ANODIZING
4.1. Regular Anodizing vs. Conductive Anodizing
Conventional anodizing is an electrolytic oxidation process that transforms the surface of aluminum into a hard aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) layer with excellent corrosion resistance. However, this oxide layer is insulating and does not dissipate static electricity—making it prone to ESD buildup.
To overcome this, conductive anodizing was developed. This special variant of anodizing treats the aluminum surface to maintain or enhance its conductivity, enabling it to safely dissipate electrostatic discharge (ESD).
4.2. Conductive Anodizing Process
The process is similar to standard anodizing but includes specific modifications:
-
Surface preparation: Cleaning and polishing the aluminum surface.
-
Electrolytic oxidation: Performed in acidic solutions (typically sulfuric acid or blends), with tightly controlled voltage and duration.
-
Unsealed or treated oxide layer: The anodized layer is left unsealed or treated with conductive salts to preserve electrical conductivity.
Result: A thin oxide layer with surface resistivity between 10⁶ and 10⁹ Ω, meeting ESD standards.
4.3. Applications in Electronics Cleanrooms
Due to higher cost and complex processing, conductive anodizing is mainly used in high-end applications, including:
-
Precision aluminum components in semiconductor manufacturing equipment and electronic modules.
-
Aluminum housings for high-end electronic devices requiring both ESD protection and a sleek, durable finish.
-
Aerospace and defense industries, where lightweight aluminum also needs to dissipate static electricity for safety.
In electronics cleanrooms, conductive anodizing is typically applied to premium aluminum components rather than general-purpose equipment.
4.4. Pros & Cons
Advantages:
-
Extremely high mechanical durability; excellent abrasion and corrosion resistance.
-
Retains natural metallic texture for a premium aesthetic.
-
Long-term stability with minimal maintenance compared to ESD paint.
Disadvantages:
-
Much higher cost than ESD powder coating.
-
Complex manufacturing process with limited suppliers.
-
Only applicable to aluminum and its alloys (not usable on steel or iron).
Summary:
Conductive anodizing is a premium ESD control solution, ideal for high-precision aluminum parts and high-end electronic equipment. Though less common than ESD powder coating, it is superior in applications requiring durability, aesthetics, and brand value.
5. COMPARISON: ESD POWDER COATING VS. CONDUCTIVE ANODIZING
Having explored each technology, the key question becomes: which is more suitable for electronics cleanrooms—ESD powder coating or conductive anodizing? Both can dissipate static charges, but differ in nature, process, and application.
5.1. Nature
-
ESD powder coating: An external coating—applying a special powder with conductive additives.
-
Conductive anodizing: An intrinsic transformation—modifying the aluminum surface itself into a conductive oxide layer.
5.2. ESD Performance
-
ESD coating: Easy to control surface resistivity between 10⁵ and 10⁹ Ω; compliant with IEC 61340 standards.
-
Conductive anodizing: Also achieves 10⁶ to 10⁹ Ω, but requires a stricter process and has fewer suppliers.
5.3. Applications
-
ESD coating: Ideal for workbenches, carts, racks, and floors—components that are mass-produced at reasonable costs.
-
Conductive anodizing: Suitable for high-end aluminum parts, electronic housings, and precision modules.
5.4. Cost & Durability
-
ESD coating: Low to moderate cost; the coating can chip and needs periodic inspection.
-
Conductive anodizing: High cost, but superior durability and abrasion resistance with minimal maintenance.
Comparison Table
| Criteria |
ESD Powder Coating |
Conductive Anodizing |
|---|---|---|
| Nature |
External coating |
Surface transformation (intrinsic) |
| Surface Resistivity |
10⁵ - 10⁹ Ω, easy to control |
10⁶ - 10⁹ Ω, stable but harder to produce |
| Mechanical Durability |
Fairly good, prone to chipping |
Excellent, outstanding wear and corrosion resistance |
| Color Options |
Wide variety (black, green, gray, etc.) |
Limited, mostly metallic tones (silver, black) |
| Applications | Workbenches, racks, carts, floors |
Aluminum housings, high-end electronics |
| Cost |
Medium, cost-effective for mass use |
High, suitable for premium products |
| Lifespan |
5-10 years, needs periodic checks |
15-30 years, highly stable |
6. WHEN TO CHOOSE ESD COATING VS. CONDUCTIVE ANODIZING?
In real-world production, there is no “perfect” solution—only the most suitable choice based on use case, cost, and product nature.
6.1. When to Choose ESD Powder Coating?
Applications: Workbenches, carts, component racks, PCB cabinets, ESD floors in assembly areas.
Reason: Cost-effective, scalable for mass production. Surface resistivity (10⁵ - 10⁹ Ω) meets international ESD safety standards—ideal for protecting entire production lines.
Example: An electronics assembly factory with hundreds of workbenches → uses ESD coating to balance cost and safety.
6.2. When to Choose Conductive Anodizing?
Applications: Aluminum housings for premium electronics, precision aluminum modules, components requiring high durability and visual appeal.
Reason: Conductive anodizing creates an ultra-durable oxide layer that reliably dissipates static and enhances product appearance—ideal for high-end branding.
Example: A company producing precision aluminum modules for medical or premium electronics → uses conductive anodizing to meet ESD standards and elevate brand value.
7. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
1. Does regular powder coating provide ESD protection?
No. Standard powder coating is an insulator and cannot dissipate static electricity. Only specially formulated ESD powder coatings with conductive additives can meet anti-static requirements for cleanroom environments.
2. Does standard anodizing offer ESD properties?
No. Regular anodizing creates an aluminum oxide layer that is completely insulating. To achieve ESD protection, conductive anodizing with a specialized process must be used.
3. How long does ESD powder coating last?
The average lifespan of ESD powder coating is 5-10 years, depending on the environment. However, the coating can chip if subjected to strong impacts. Regular testing of surface resistivity is essential to ensure continued ESD performance.
4. Is conductive anodizing widely used?
Conductive anodizing is less common than ESD powder coating. It is mainly used in high-end aluminum products for the electronics, aerospace, and medical industries. Due to its higher cost and complex process, it's not widely applied to mass-market industrial equipment.
5. Which technology is preferable for electronics cleanrooms?
It depends on the application:
-
ESD powder coating is suitable for workbenches, racks, carts, and floors—where large quantities and cost-efficiency are needed.
-
Conductive anodizing is ideal for high-end aluminum components and housings that require durability and aesthetics.
In practice, companies can combine both technologies to build a comprehensive ESD protection system in cleanroom environments.
8. CONCLUSION
In electronics cleanroom environments, controlling electrostatic discharge (ESD) is not just a technical requirement—it is critical to maintaining product quality and protecting brand reputation. Between the two popular technologies—ESD powder coating and conductive anodizing—each has its own strengths.
-
ESD powder coating is suitable for general industrial equipment such as workbenches, racks, carts, and anti-static flooring. Its advantages include reasonable cost, ease of application, and compliance with international ESD standards.
-
Conductive anodizing is ideal for high-end aluminum components and housings, offering superior mechanical durability, wear resistance, visual appeal, and brand value.
Combining both technologies in the same cleanroom system yields optimal results: ESD powder coating for general equipment, and conductive anodizing for precision components.
If your company is looking for effective ESD protection solutions for electronics cleanrooms, contact VCR.
We provide everything from internationally certified ESD powder coatings to specialized anodizing solutions—helping your factory meet ESD certification requirements and operate safely and efficiently.
Hotline: 090.123.9008
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://phongsachdientu.com
Diep VCR
Vietnam Cleanroom (VCR) là một doanh nghiệp hàng đầu tại Việt Nam chuyên cung cấp thiết bị và giải pháp phòng sạch. Với hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm phục vụ các dự án phòng sạch đạt tiêu chuẩn GMP, VCR tự hào mang đến các thiết bị kỹ thuật cao như: đồng hồ chênh áp, khóa liên động, đèn phòng sạch, Pass Box, FFU (Fan Filter Unit), buồng cân, HEPA Box, Air Shower, cửa thép phòng sạch, tủ cách ly (ISOLATOR), và nhiều loại phụ kiện chuyên dụng khác
Không chỉ là nhà cung cấp thiết bị, VCR còn là đơn vị phân phối độc quyền các sản phẩm từ các thương hiệu quốc tế như LENGE và BLOCK Technical, đồng thời cung cấp các giải pháp phòng sạch toàn diện cho các lĩnh vực như dược phẩm, điện tử, y tế, thực phẩm và mỹ phẩm. VCR có đội ngũ chuyên gia giàu kinh nghiệm, kiến thức chuyên sâu về phòng sạch, hỗ trợ tư vấn về tiêu chuẩn, thiết kế, thi công và vận hành phòng sạch theo chuẩn ISO, GMP, HACCP, ISO 14644
VCR hướng đến trở thành thương hiệu quốc dân trong ngành phòng sạch, với mạng lưới cung ứng rộng khắp, VCR có các văn phòng tại Hà Nội, TP. HCM, đáp ứng mọi yêu cầu từ xây dựng đến nâng cấp môi trường sản xuất đạt chuẩn
Email: [email protected]
Điện thoại: (+84) 901239008
Địa chỉ:
VP Hà Nội: 9/675 Lạc Long Quân, P. Xuân La, Q. Tây Hồ, TP. Hà Nội
VP Hồ Chí Minh: 15/42 Phan Huy Ích, P.15, Q. Tân Bình, TP.HCM
Hãy liên hệ với VCR để tìm hiểu thêm về lĩnh vực phòng sạch hiệu quả nhất nhé!