- 1. The Role of Lighting in Electronic Inspection Areas
- 2. Key Technical Factors in Lighting Design
- 3. Lighting Standards in the Electronics Industry
- 4. Recommended Lighting Types for Electronic Inspection Areas
- 5. Practical Application: Effective Lighting Layout for Inspection
- 6. Common Lighting Mistakes & How to Fix Them
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions About Inspection Lighting
- 8. Need Lighting Consultation for Your Electronics Inspection Area?
1. The Role of Lighting in Electronic Inspection Areas
Lighting plays a crucial role in all inspection, verification, and defect detection activities in the electronics industry - especially during PCB inspections, micro-component testing, solder joint assessments, or surface defect identification. Inadequate or improperly calibrated lighting can significantly compromise inspection quality.
Why is lighting important?

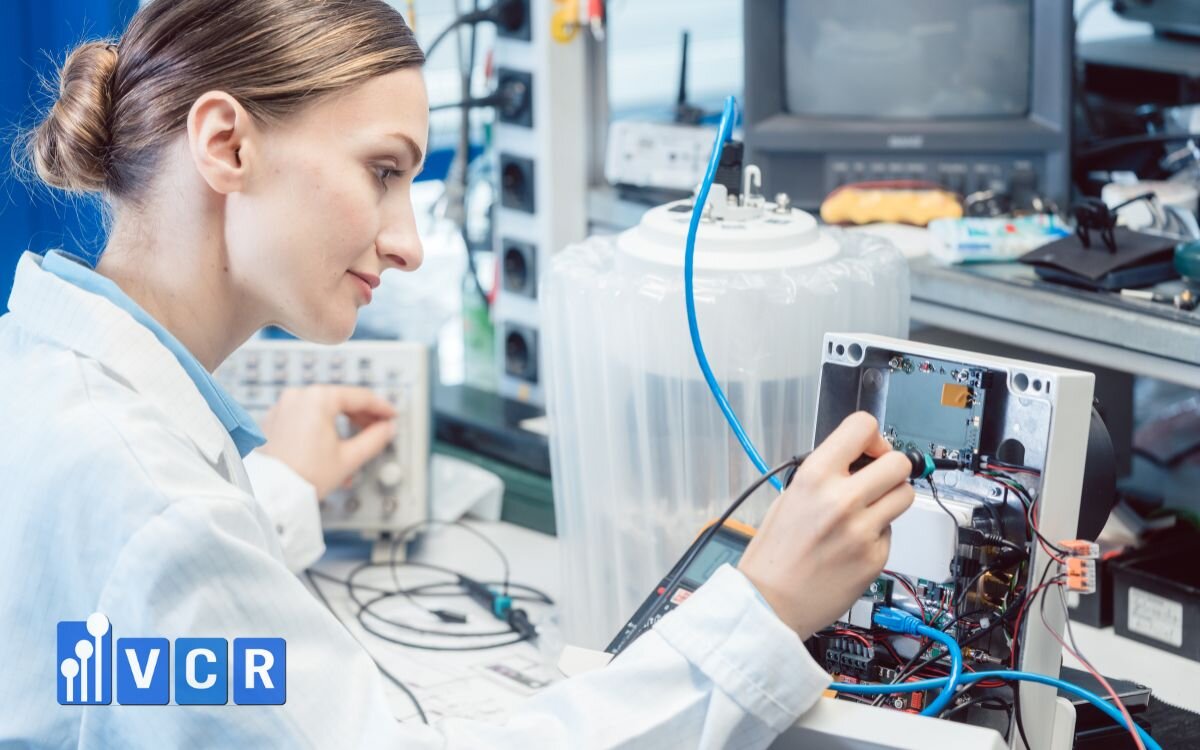
- Enhances inspection accuracy: Technicians need sufficient lighting to clearly see solder joints, cracks, misaligned components, or micro-defects on circuit boards.
- Reduces eye strain - improves productivity: Proper lighting minimizes visual fatigue, allowing inspectors to work efficiently over extended periods.
- Lowers error rate - increases reliability: Substandard lighting can lead to overlooked defects or misjudged component conditions.
Consequences of substandard lighting
|
Lighting Issue |
Impact on Electronics Inspection |
|
Insufficient illuminance |
Missed micro-defects, inaccurate assessments |
|
Uneven lighting distribution |
Causes shadows, color shifts during inspection |
|
Inappropriate color temperature |
Incorrect perception of PCB/component colors |
|
Low CRI (< 80) |
Inability to differentiate fine color details |
2. Key Technical Factors in Lighting Design
To ensure effective inspection in electronics manufacturing, the lighting system must not only be bright enough but also meet specific standards in color temperature and color rendering. Below are the minimum technical requirements for lighting in inspection areas.
Illuminance (Lux) - The more detail, the more light needed
|
Inspection Area |
Recommended Illuminance (lux) |
|
General visual inspection |
500 - 750 lux |
|
Detailed inspection (solder, SMT) |
800 - 1500 lux |
|
Micro-defect, particle inspection |
≥ 2000 lux |
Tip: Use a lux meter to accurately measure illuminance at each workstation instead of relying solely on theoretical light fixture specifications.
Color Temperature (CCT): 5000K - 6500K
- This range mimics daylight, helping technicians perceive true colors and defects more naturally.
- Temperatures below 4000K produce warm (yellow) light, which distorts vision; above 7000K produces cold (blue) light that may cause eye strain.
Color Rendering Index (CRI): ≥ 90
- A higher CRI (Color Rendering Index) ensures better color fidelity.
- CRI ≥ 90 enables technicians to:
- Detect color mismatches in components
- Identify burn marks or black spots
- Spot small soldering defects
See more: How to choose the right Pass Box for electronic clean room
3. Lighting Standards in the Electronics Industry
In electronics manufacturing environments, lighting is not just a support element but a technical requirement governed by international standards. The following are key standards often referenced:
ISO 14644 - Cleanroom Lighting Requirements
- ISO 14644-4 (Design and construction of cleanrooms) requires working areas to have ≥ 500 lux, evenly distributed and glare-free.
- Lighting must not emit dust, ozone, or disrupt cleanroom conditions.
- Fixtures should be flush-mounted with high IP rating, minimizing gaps to prevent secondary contamination.

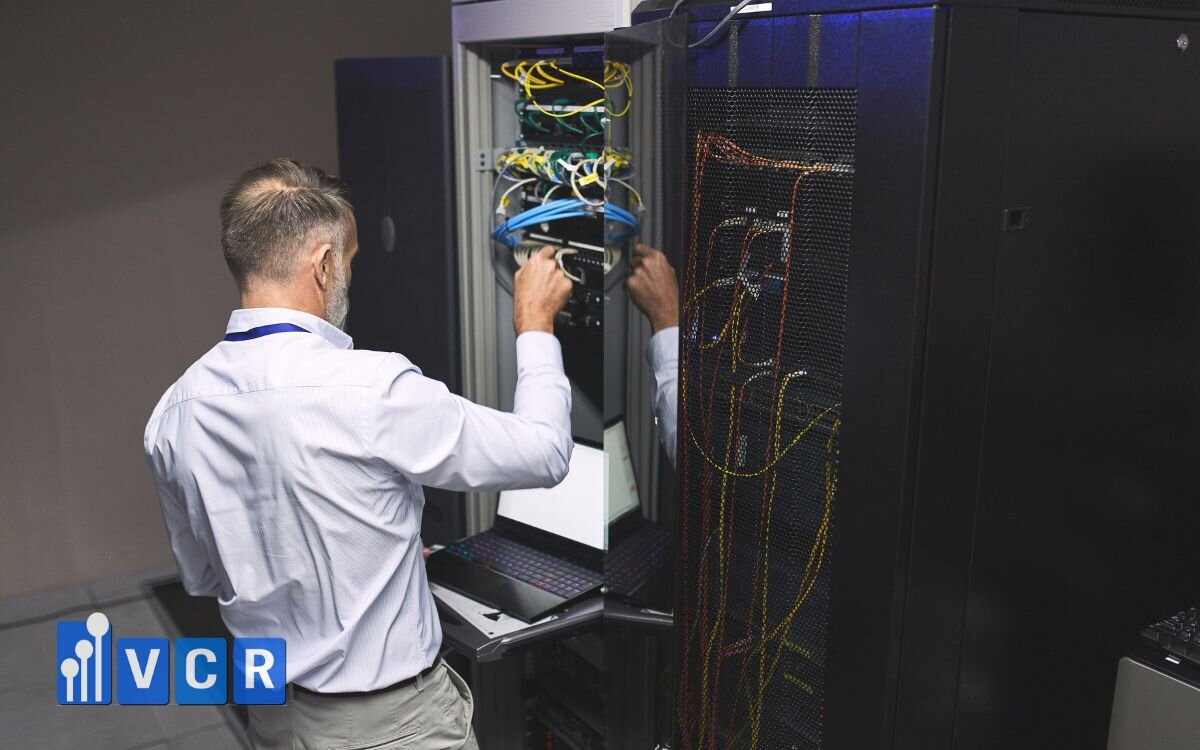
IEC 61340 & IPC-A-610 - PCB Inspection Requirements
- IEC 61340 covers ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) control, including lighting that does not accumulate static charge.
- IPC-A-610, the standard for acceptability of electronic assemblies, specifies lighting requirements to detect:
- Non-compliant solder joints
- Misaligned components
- Micro-scale physical damage
→ According to IPC, inspection zones should have a minimum of 1000 lux, CRI ≥ 90, and diffuse lighting to avoid shadows.
ESD Area Lighting Requirements
- Fixtures must avoid generating static electricity; plastic materials with poor conductivity should not be used.
- Choose lighting with metal housings and anti-static designs for safer ESD environments.
- Ensure even lighting distribution to prevent inaccurate handling or inspection caused by light imbalances.
4. Recommended Lighting Types for Electronic Inspection Areas
Choosing the right lighting fixtures is critical to ensuring inspection quality in electronics manufacturing environments. Below are the types of lighting recommended for error detection, PCB testing, and microcomponent analysis.
1. High-power LED Panels, CRI ≥ 90
Advantages:
- Provides uniform illumination across the work surface
- High color rendering index (CRI) enables accurate detection of small defects and color deviations
Recommended specifications:
- Power: 40W - 60W
- Size: 600×1200 mm or 600×600 mm
- Light color: Neutral white (5000K - 6500K)
2. Anti-glare Lighting (UGR < 19)
- UGR (Unified Glare Rating) indicates the degree of visual glare.
- Fixtures with UGR < 19 reduce eye strain for technicians, especially during long shifts.
- Ideal for general visual inspections and image analysis stations.
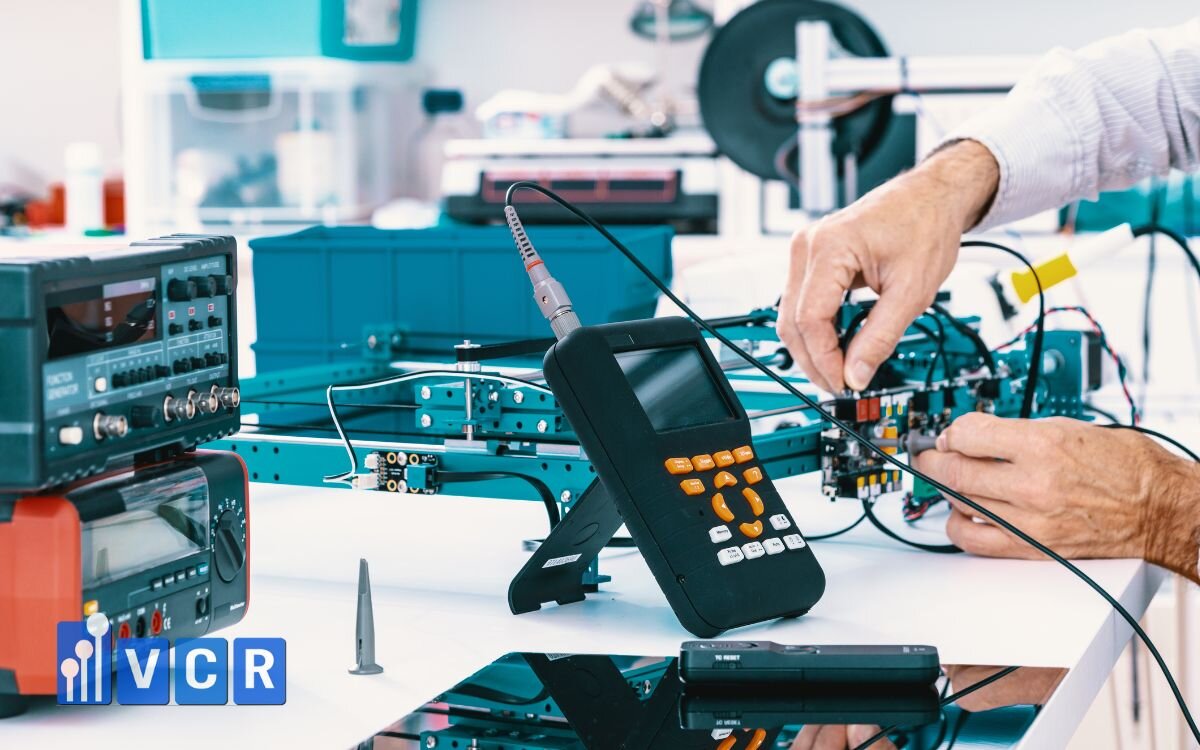

3. Cleanroom-rated Fixtures (IP65 or higher)
- Must meet ISO 7 - ISO 8 cleanroom requirements for dust and moisture resistance.
- Should be flush-mounted to prevent contamination from crevices or particles.
- Housings should be made of tempered glass and anodized aluminum for easy cleaning and long-term durability.
Suggested Lighting Products
|
Light Type |
Key Specifications |
Application Area |
|
LED Panel 600×1200 |
60W, CRI ≥ 90, CCT 5500K |
PCB test benches |
|
Recessed LED IP65 |
CRI 95, UGR < 19 |
Detail inspection stations |
|
Task Lighting |
Focused, adjustable beam |
Micro-inspection zones |
See more: ISO 5 quality control room design
5. Practical Application: Effective Lighting Layout for Inspection
Compliant lighting depends not only on the quality of fixtures but also on how they are arranged in real workspaces. Below are proven layout principles for electronic inspection areas.
Grid-style lighting layout for test benches
Using a grid lighting layout ensures:
- Uniform light distribution across the entire area
- Minimization of dark or overly bright zones that can cause visual fatigue
Recommended spacing:
Horizontal and vertical spacing between fixtures: 1.2 - 1.5 meters
Best suited for large PCB inspection zones or SMT lines.
Fixture spacing - ceiling height - beam direction
- Ideal vertical distance from fixture to work surface: 2.2 - 2.6 meters
- Beam direction: Perpendicular downward to avoid shadows
- For ceilings higher than 3 meters, use higher-power fixtures or reflective panels
Integrating task lighting for micro-inspection
Use dedicated desk lamps for concentrated lighting at critical points:
- Inspecting small SMD components
- Analyzing solder joints or electrical leakage
Task lighting requirements:
- Illuminance ≥ 2000 lux
- Glare-controlled reflectors, adjustable beam angles
- Anti-static housing (preferably metal)
Combining general lighting with task lighting is the optimal solution to ensure full-area illumination while providing precision lighting at key inspection zones.
See more: Common mistakes when inspecting electronic clean rooms
6. Common Lighting Mistakes & How to Fix Them
Despite having invested in lighting systems for inspection areas, many electronics manufacturers still encounter issues that affect inspection accuracy and technician eye health. Below are common mistakes and corresponding solutions.
1. Uneven lighting causes eye strain
- Causes:
- Inconsistent fixture layout, creating dark or overlit zones
- Strong light absorption from work surfaces or walls
- Consequences:
- Eye fatigue for technicians, reduced inspection accuracy
- Increased rate of overlooked defects due to inconsistent lighting
- Solutions:
- Design a grid-based lighting layout with consistent fixture spacing
- Paint walls and ceilings in light colors (white or matte silver) to enhance light reflection
2. Using overly warm or overly cool lighting
- Causes:
- Inappropriate color temperature (CCT < 4000K or > 7000K)
- Consequences:
- Color distortions in PCBs and components
- Difficulty identifying micro-defects or physical damage
- Solutions:
- Use fixtures with a CCT between 5000K - 6500K (neutral white light)
- Audit the entire lighting system and replace fixtures that fall outside the ideal range
3. Lack of routine lighting performance checks
- Causes:
- No regular lux measurement or light aging evaluation
- No maintenance protocol in place for lighting systems
- Consequences:
- Lighting degrades over time without being replaced
- Inspection areas fail to meet standards without detection
- Solutions:
- Implement a lux check routine every 3-6 months using a lux meter
- Log lighting levels and replace fixtures when output drops below 80% of the original specification
See more: ESD Powder Coating or Anodizing – Effective Anti-Static Solution for Electronic Clean Rooms
7. Frequently Asked Questions About Inspection Lighting
Are LED Panels suitable for electronics inspection?
→ Yes, provided they have a CRI ≥ 90 and a minimum illuminance of 1000 lux. High-power LED Panels with neutral white light (5000K - 6500K) are ideal for inspecting PCBs, SMD components, and solder joints.
How many lux are needed for inspecting SMT board defects?
→ According to IPC-A-610, SMT defect inspection requires at least 1500 lux. For very small components (0402 and smaller), task lighting with ≥ 2000 lux is recommended.
Is it necessary to have dedicated lights for each inspection bench?
→ Yes. Integrating task lighting for each workstation allows technicians to adjust the beam angle and intensity as needed, improving accuracy, reducing eye strain, and minimizing overlooked defects.
8. Need Lighting Consultation for Your Electronics Inspection Area?
Designing a lighting system that meets inspection standards not only improves defect detection but also enhances productivity and reliability across PCB inspection processes.
Contact VCR’s technical team today for tailored lighting solutions for your electronics factory - from selecting fixtures to layout design and on-site lux verification.
Hotline: 090.123.9008
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://phongsachdientu.com/
Diep VCR
Vietnam Cleanroom (VCR) là một doanh nghiệp hàng đầu tại Việt Nam chuyên cung cấp thiết bị và giải pháp phòng sạch. Với hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm phục vụ các dự án phòng sạch đạt tiêu chuẩn GMP, VCR tự hào mang đến các thiết bị kỹ thuật cao như: đồng hồ chênh áp, khóa liên động, đèn phòng sạch, Pass Box, FFU (Fan Filter Unit), buồng cân, HEPA Box, Air Shower, cửa thép phòng sạch, tủ cách ly (ISOLATOR), và nhiều loại phụ kiện chuyên dụng khác
Không chỉ là nhà cung cấp thiết bị, VCR còn là đơn vị phân phối độc quyền các sản phẩm từ các thương hiệu quốc tế như LENGE và BLOCK Technical, đồng thời cung cấp các giải pháp phòng sạch toàn diện cho các lĩnh vực như dược phẩm, điện tử, y tế, thực phẩm và mỹ phẩm. VCR có đội ngũ chuyên gia giàu kinh nghiệm, kiến thức chuyên sâu về phòng sạch, hỗ trợ tư vấn về tiêu chuẩn, thiết kế, thi công và vận hành phòng sạch theo chuẩn ISO, GMP, HACCP, ISO 14644
VCR hướng đến trở thành thương hiệu quốc dân trong ngành phòng sạch, với mạng lưới cung ứng rộng khắp, VCR có các văn phòng tại Hà Nội, TP. HCM, đáp ứng mọi yêu cầu từ xây dựng đến nâng cấp môi trường sản xuất đạt chuẩn
Email: [email protected]
Điện thoại: (+84) 901239008
Địa chỉ:
VP Hà Nội: 9/675 Lạc Long Quân, P. Xuân La, Q. Tây Hồ, TP. Hà Nội
VP Hồ Chí Minh: 15/42 Phan Huy Ích, P.15, Q. Tân Bình, TP.HCM
Hãy liên hệ với VCR để tìm hiểu thêm về lĩnh vực phòng sạch hiệu quả nhất nhé!